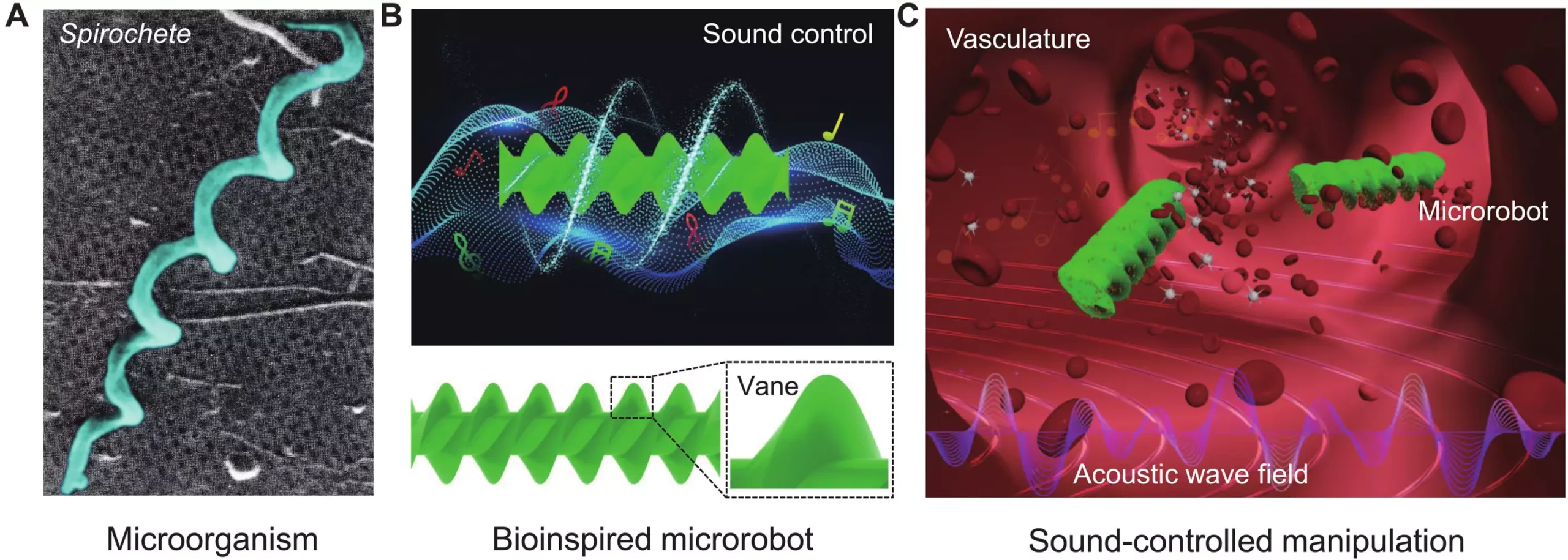
The field of medical research has long sought after a more precise method of drug delivery, one that targets specific areas of the body in order to minimize side effects. Current efforts involve the use of magnet-controlled robots, but these solutions lack the necessary precision control. However, a team of robotic and acoustic engineers from the Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems, ETH Zurich, and Institut für Theoretische Physik, Center for Soft Nanoscience, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, has recently developed a groundbreaking microrobot propelled by sound waves. In their published paper in Science Advances, the team details the design of their innovative robots and their impressive capabilities.
Unlike conventional methods utilizing external magnets, this team harnessed sound waves as a means of propulsion. The microrobot consists of a 3D printed, non-toxic polymer in the shape of a corkscrew. After placing the corkscrew in a glass tube filled with either water or alcohol, the researchers fired sound waves at it. The sound waves caused the molecules in the liquid to vibrate, creating a vortex that propels the robot forward. Moreover, the team discovered that changing the features of the sound waves allowed them to adjust the robot’s speed and direction. By increasing the sound wave frequencies, the researchers were even able to propel the robot upwards through a 45-degree tilted tube.
The microrobot developed by this research team offers exciting possibilities for drug delivery within the human body. By utilizing sound waves, it becomes possible to navigate through narrow tubes, simulating human blood vessels with greater accuracy. The team’s next objective involves testing their microrobot in tubes made of more flexible materials, which replicates real-world conditions more effectively. Additionally, the researchers are working on an acoustic helmet that they believe will provide even greater control over the robot.
The use of sound waves as a propelling force for microrobots presents several advantages. Unlike magnet-controlled robots, sound waves provide more precise control over speed and direction. This level of control is crucial for drug delivery, as it allows for targeted medication administration and reduces the risk of unwanted side effects. Furthermore, sound waves offer a safer alternative, as they can be easily absorbed by the body without causing harm.
The development of a microrobot propelled by sound waves represents a significant breakthrough in the field of drug delivery. This innovative approach offers greater precision control and the potential to target specific areas within the body. With further advancements in flexible tube testing and the development of an acoustic helmet, this technology could revolutionize the way medications are administered, minimising side effects and improving patient outcomes. The future looks promising for the integration of microrobots into medical practices, bringing us one step closer to more effective and personalized healthcare.

Leave a Reply